Intracerebroventricular Baclofen Therapy for Chronic Pelvic Pain in Cerebral Palsy: A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46900/apn.v7i3.322Keywords:
cerebral palsy, vulvodynia, intraventricular baclofen, dystonia, spasticityAbstract
Introduction: Although pain is frequent among patients with cerebral palsy (CP), vulvodynia is an uncommon finding. Its diagnosis is underrated in this population and its treatment is challenging, due to uncertainty in pathophysiological mechanisms of the symptom. The management of this rare combination of relevant sensorial and motor components requires a skilled multidisciplinary team capable of offering and testing all available forms of treatment, since this pain carries high levels of suffering and incapacity, and patients with CP usually have many other chronic and severe comorbidities.
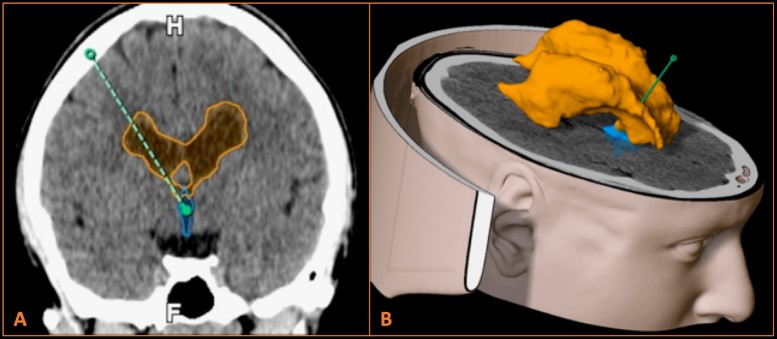
Case presentation: This is a 14-year-old girl with mixed (hyperkinetic and spastic) CP, with minimal cognitive impairment, and classified as Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) level V. She failed all available conservative treatments for a longstanding and disabling vulvodynia. Local injections, including toxin botulinum failed to provide relief. After responding to an intrathecal baclofen trial, a baclofen pump was implanted with the catheter positioned within the third ventricle through navigation guidance. She experienced complete pain relief, and spasticity improvement as well. During the 6 months of follow-up, patient was pain free. Her quality of life also improved with the therapy during the follow-up period.
Conclusion: Intracerebroventricular baclofen therapy may be a viable option for managing chronic pain associated with spastic-dystonic symptoms in cerebral palsy.
; vulvodynia; ; dystonia; spasticity
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Guilherme Corsaletti Gregório, Fabio Okuda Furokawa, Eduardo Joaquim Lopes Alho, Luciano Furlanetti, Bernardo Assumpção de Monaco

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

When publishing in Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery journal, authors retain the copyright of their article and agree to license their work using a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC BY 4.0), thereby accepting the terms and conditions of this license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode).
The CC BY 4.0 license terms applies to both readers and the publisher and allows them to: share (copy and redistribute in any medium or format) and adapt (remix, transform, and build upon) the article for any purpose, even commercially, provided that appropriate credit is given to the authors and the journal in which the article was published.
Authors grant Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery the right to first publish the article and identify itself as the original publisher. Under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license, authors allow the journal to distribute the article in third party databases, as long as its original authors and citation details are identified.





























