Bilateral pallidotomy to status dystonicus in children from public health system: case series and technical notes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46900/apn.v7i3.317Keywords:
dystonia, children, pallidotomyAbstract
Background: Dystonia is the second most common pediatric movement disorder after spasticity and may occasionally present as status dystonicus (SD), a life-threatening neurological emergency. Medical management of SD remains challenging and sometimes ineffective, therefore neurosurgical alternatives such as intrathecal/intraventricular baclofen administration, deep brain stimulation and pallidotomy may be needed in severe refractory cases.
Objective: To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of bilateral pallidotomy in children with severe, drug-resistant dystonia, including cases of status dystonicus.
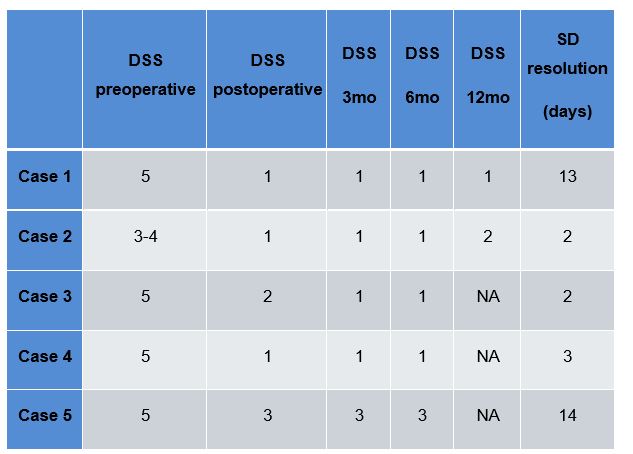
Methods: This retrospective study analyzed five pediatric patients (mean age: 8.23 years) treated between January 2024 and February 2025 at a tertiary public hospital in Brazil. All had a Dystonia Severity Score (DSS) ≥3 and underwent bilateral pallidotomy. Clinical outcomes, DSS changes, medication use, and postoperative medications were assessed.
Results: All patients showed clinical improvement, including resolution of status dystonicus. The average time to symptom stabilization was 6.8 days. The number of medications decreased by 22.86% postoperatively. No major complications were observed. Two patients had minor postoperative radiologic findings without clinical repercussions.
Conclusion: Bilateral pallidotomy appears to be a safe and effective option in the management of severe, drug-resistant dystonia in children, particularly status dystonicus. These preliminary results highlight its potential role in selected pediatric cases. Larger studies are needed to confirm long-term efficiency and safety of bilateral pallidotomy in this context
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Antônio Jorge Barbosa de Oliveira, Patricia Dumke da Silva Moller, Bruna Sousa Rodrigues, Kesia Priscilla Omena Cardoso, Arthur de Melo Monteiro Bastos, Rayane Gomes de Sousa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

When publishing in Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery journal, authors retain the copyright of their article and agree to license their work using a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC BY 4.0), thereby accepting the terms and conditions of this license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode).
The CC BY 4.0 license terms applies to both readers and the publisher and allows them to: share (copy and redistribute in any medium or format) and adapt (remix, transform, and build upon) the article for any purpose, even commercially, provided that appropriate credit is given to the authors and the journal in which the article was published.
Authors grant Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery the right to first publish the article and identify itself as the original publisher. Under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license, authors allow the journal to distribute the article in third party databases, as long as its original authors and citation details are identified.





























