Neurectomy for treatment of pediatric spasticity: a review of literature
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46900/apn.v7i3.313Keywords:
pediatrics, muscle spasticity, denervationAbstract
Introduction: Spasticity in the pediatric population presents significant management challenges. The aim of this study was to review the current literature on the use of selective neurectomy for treating pediatric spasticity. It is important to analyze children as a distinct group, as the selection criteria differ from those used in adults, and the procedure affects not only spasticity but also the overall development of the child.
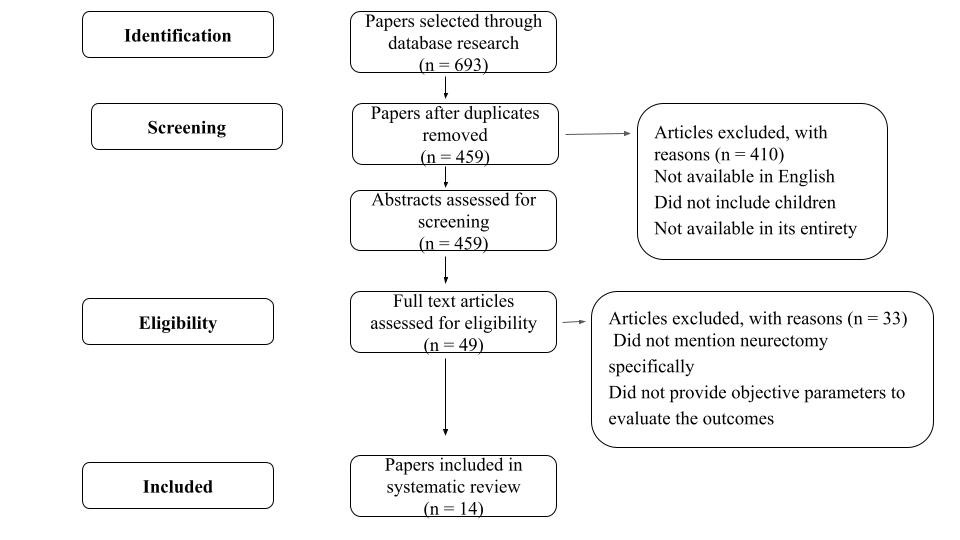
Methods: After a PubMed database search and applying inclusion criteria, we identified 14 relevant studies for this review. The following parameters were analyzed: patient age, number of participants, follow-up duration, Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) scores, goniometry/passive range of motion (PROM), and motor function.
Results: There was considerable variability in the first three parameters (age, sample size, and follow-up period). All included studies reported improvements in spasticity, range of motion, and motor function when these outcomes were assessed. However, the methods used to evaluate these outcomes varied, limiting direct comparisons across studies.
Conclusion: Although few studies on selective neurectomy for pediatric spasticity were found, all demonstrated significant improvements in parameters associated with enhanced quality of life. These findings highlight the need for further research focused specifically on this population.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Stephanie Oliveira Fernandes de Bulhões, Ricardo de Amoreira Gepp, Márcio de Mendonça Cardoso

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

When publishing in Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery journal, authors retain the copyright of their article and agree to license their work using a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC BY 4.0), thereby accepting the terms and conditions of this license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode).
The CC BY 4.0 license terms applies to both readers and the publisher and allows them to: share (copy and redistribute in any medium or format) and adapt (remix, transform, and build upon) the article for any purpose, even commercially, provided that appropriate credit is given to the authors and the journal in which the article was published.
Authors grant Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery the right to first publish the article and identify itself as the original publisher. Under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license, authors allow the journal to distribute the article in third party databases, as long as its original authors and citation details are identified.





























