Surgical Treatment of Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis of Cervical Spine: Case-Report and Systematic Review of Literature
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46900/apn.v7i1.270Keywords:
Langerhans-cell histiocytosis, Extradural tumor, spine tumor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NeurosurgeryAbstract
Background: Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a rare disease involving the cervical spine. This condition is present firstly in the thoracic spine, commonest, followed by the lumbar spine and cervical spine. In Langerhans cell histiocytosis there is excessive proliferation of pathologic Langerhans cells. It is commonly found in males with a ratio of 2.5:1. The etiology of LCH is unknown. There are three defined entities classified on their severities. Letterer-Siwe disease involves multiple organs, Hand-Schuller-Christian disease presents with bony lesions and endocrine abnormalities, and eosinophilic granuloma (EG) presents with isolated bony lesions. We describe a case-report a girl with Langerhans cell histiocytosis in cervical vertebrae.The objective of this study is to show the rare case of Cervical Spine Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis.
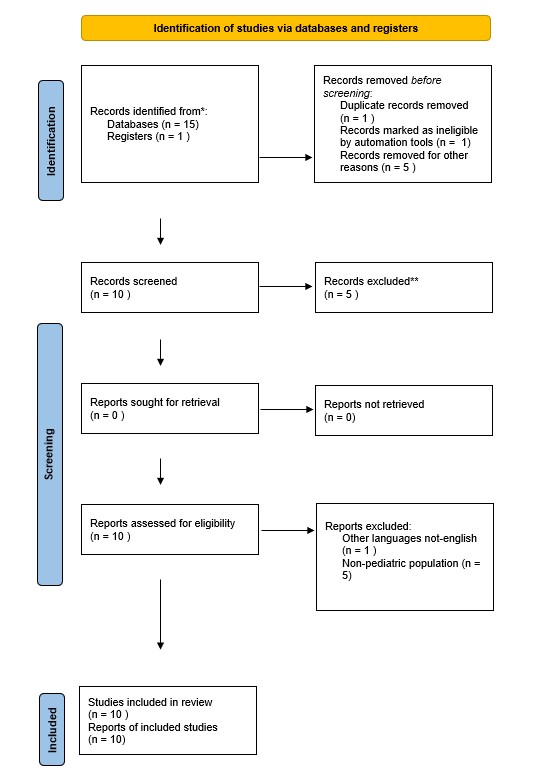
Method: We were a literature review with inclusion and exclusion criteria and we described a case-report.
Case-Report: A 9-month-old girl had neck pain associated with right upper limb weakness. Imaging showed infiltrative and expansive lesions in the vertebral body from C1 to C6 with spinal cord and root compression. The patient underwent a laminectomy from C2 to C5. Histopathological was suggestive of LCH.
Conclusion: Despite the rarity of the disease, Langerhans cell histiocytosis can be treated with a surgical approach when neurologic deficits are present.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Breno Barbosa, Paulo Ronaldo Jube Ribeiro

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

When publishing in Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery journal, authors retain the copyright of their article and agree to license their work using a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC BY 4.0), thereby accepting the terms and conditions of this license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode).
The CC BY 4.0 license terms applies to both readers and the publisher and allows them to: share (copy and redistribute in any medium or format) and adapt (remix, transform, and build upon) the article for any purpose, even commercially, provided that appropriate credit is given to the authors and the journal in which the article was published.
Authors grant Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery the right to first publish the article and identify itself as the original publisher. Under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license, authors allow the journal to distribute the article in third party databases, as long as its original authors and citation details are identified.





























